
❤️ Heart-এর বাহ্যিক গঠন
External Structure of the Heart
📍 অবস্থান (Location)
- হৃৎপিণ্ড অবস্থিত thoracic cavity-র mediastinal space-এর ventral (পেটের দিকের) পাশে
- ➤ দুই ফুসফুসের (lungs) মাঝে
- Left lung-এ একটি cardiac notch থাকে → কারণ সেখানে হৃৎপিণ্ড ঢুকে থাকে
💡 হৃৎপিণ্ড thoracic cavity-র মধ্যখানে অবস্থিত, sternum এর পিছনে
📏 আকার (Size)
5 x 3.5 ইঞ্চি
(দৈর্ঘ্য x প্রস্থ)
⚖️ ওজন (Weight)
~300 গ্রাম
(প্রাপ্তবয়স্ক মানুষের)
🔺 আকৃতি ও অবস্থান (Shape & Tilt)
- হার্টের আকৃতি ত্রিভুজাকৃতি (triangular)
- উপরের চওড়া অংশ (broad base) → ডান দিকে সামান্য ঝুঁকে থাকে
- নিচের সরু অংশ (apex) → বাম দিকে ঝুঁকে থাকে
📝 Apex = left side-এ 5th intercostal space-এ দেখা যায় (midclavicular line)
🧥 Pericardial Membrane (পরিকার্ডিয়াল ঝিল্লি)
হৃদপিণ্ডকে ঘিরে থাকা দ্বিস্তরবিশিষ্ট আবরণ (double-layered covering):
Outer Layer
Parietal Pericardium
- white fibrous connective tissue
- মজবুত ও রক্ষাকারী স্তর
Inner Layer
Visceral Pericardium (Epicardium)
- serous membrane
- সরাসরি হৃদপিণ্ডের উপর লেগে থাকে
💧 Pericardial Cavity & Fluid
- দুই স্তরের মাঝে ফাঁকা জায়গা = Pericardial cavity
- এই cavity-তে থাকে Pericardial fluid
Pericardial Fluid-এর কাজ:
- স্নেহাক্ত তরল (lubricating fluid)
- ঘর্ষণ (friction) কমিয়ে দেয়
- আঘাত ও শুকিয়ে যাওয়া থেকে রক্ষা করে
🏥 ক্লিনিক্যাল তাৎপর্য
Pericarditis (পরিকার্ডাইটিস)
পরিকার্ডিয়ামের প্রদাহ হলে:
- Pericardial fluid বেড়ে যায়
- হৃৎপিণ্ডের কাজে বাধা সৃষ্টি করতে পারে
- বুক ব্যথা ও শ্বাসকষ্ট হয়
💡 Cardiac tamponade একটি জরুরি অবস্থা যেখানে অতিরিক্ত তরল হৃৎপিণ্ডকে চাপ দেয়
🎨 রং ও আকার (Color & Shape)
রং
ফিকে গোলাপি (Pinkish)
আকৃতি
শঙ্কু আকৃতি (Conical)
🔺 হৃদপিণ্ডের প্রধান অংশ
🔹 Base (Auricular Part)
- হৃদপিণ্ডের চওড়া উপরের অংশ
- এখানে auricles বা atria থাকে
- এটাকেই বলা হয় auricular part বা base
💡 Atria = উপরের প্রকোষ্ঠ, রক্ত গ্রহণের জন্য বিশেষায়িত
🔸 Apex (Ventricular Tip)
- হৃদপিণ্ডের নিচের সরু অংশ
- এখানে থাকে ventricles
- এর একদম নিচের মাথার অংশকে বলে apex
💡 Apex beat = 5th intercostal space, midclavicular line-এ অনুভব করা যায়
🫀 a. Auricles (অলিন্দ / Atria)
গঠন ও বৈশিষ্ট্য
- আকারে ছোট এবং রঙে গা dark বা গাঢ়
- প্রাচীর পাতলা (thin)
- রক্ত চাপ (blood pressure) কম থাকে
ডান অলিন্দ
- আকারে বড়
- সমস্ত systemic venous রক্ত গ্রহণ করে
- SVC, IVC ও coronary sinus থেকে রক্ত পায়
বাম অলিন্দ
- আকারে ছোট
- পালমোনারি শিরা থেকে রক্ত পায়
- Left atrial appendage থাকে
b. Ventricles (নিলয়)
গঠন ও বৈশিষ্ট্য
- আকারে চওড়া (broad)
- মাংসপেশিতে সমৃদ্ধ (muscular)
- রঙে হালকা (light-coloured)
- প্রাচীর auricles-এর তুলনায় অনেক বেশি পুরু
ডান নিলয়
- আকারে ছোট (smaller)
- প্রাচীর তুলনামূলকভাবে পাতলা
- ফুসফুসে রক্ত পাঠায় (pulmonary circulation)
- চাপ কম (~25 mmHg)
বাম নিলয়
- আকারে বড় ও প্রাচীর পুরু
- সারা শরীরে রক্ত পাঠায় (systemic circulation)
- চাপ বেশি (~120 mmHg)
- Apex গঠন করে
ঝুঁকে থাকা অবস্থান (Tilted Orientation)
Ventricular part বা নিম্নাংশটি obliquely right দিকে ঝুঁকে থাকে। বাম নিলয় apex গঠন করে।
🏥 ক্লিনিক্যাল তাৎপর্য
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH)
দীর্ঘস্থায়ী উচ্চ রক্তচাপে:
- বাম নিলয়ের প্রাচীর অস্বাভাবিক পুরু হয়
- কার্ডিয়াক আউটপুট কমে যেতে পারে
- ECG-তে বিশেষ পরিবর্তন দেখা যায়
💡 Right ventricle failure → Pulmonary hypertension হতে পারে
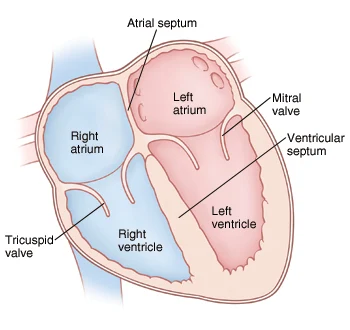
🫀 হৃদপিণ্ডের অভ্যন্তরীণ গঠন
Internal Structure of Heart
🧩 হৃদপিণ্ডের প্রাচীরের স্তরসমূহ
I. Epicardium (এপিকার্ডিয়াম)
- বাইরের স্তর (outermost layer)
- Mesodermal origin
- তৈরি হয়েছে simple squamous epithelium দিয়ে
- এটি visceral layer of pericardium হিসেবেও পরিচিত
💡 Coronary arteries এই স্তরে অবস্থিত
II. Myocardium (মায়োকার্ডিয়াম)
- মাঝের স্তর (middle layer)
- সবচেয়ে পুরু (thickest) স্তর
- Mesodermal origin
- তৈরি হয়েছে cardiac muscle fibers দিয়ে
- এই মাংসপেশি striated হলেও involuntary (ইচ্ছাধীন নয়)
💡 Left ventricle-এ সবচেয়ে পুরু (10-15 mm)
III. Endocardium (এন্ডোকার্ডিয়াম)
- সবচেয়ে ভিতরের স্তর (innermost layer)
- Endodermal origin
- তৈরি simple squamous epithelium দিয়ে
- হৃদপিণ্ডের গহ্বরের অভ্যন্তরীণ আবরণ তৈরি করে
💡 ভালভের leaflets এই স্তর দ্বারা আবৃত
📍 2. Septum (বিভাজক প্রাচীর)
হৃদপিণ্ডের ডান ও বাম দিকের কক্ষগুলিকে আলাদা রাখে যে প্রাচীরগুলো, তাদের বলে septum।
a. Interatrial Septum (ইন্টারঅট্রিয়াল সেপটাম)
- ডান ও বাম অলিন্দের (atria) মাঝে বিভাজক
- বাম দিকে সামান্য সরানো (shifted towards left) থাকে
- ফলে ডান অলিন্দ তুলনামূলকভাবে বড় হয়
💡 Fetal life-এ foramen ovale থাকে যা জন্মের পর বন্ধ হয়ে fossa ovalis গঠন করে
b. Interventricular Septum (ইন্টারভেন্ট্রিকুলার সেপটাম)
- ডান ও বাম নিলয়ের (ventricles) মাঝে বিভাজক
- দুটি অংশ থাকে:
- Membranous part (উপরের ছোট অংশ)
- Muscular part (নিচের বড় অংশ)
- বাম নিলয়ের দিকে বাঁকানো
💡 VSD (Ventricular Septal Defect) এই septum-এ ছিদ্র হলে হয়
🏥 ক্লিনিক্যাল তাৎপর্য
মায়োকার্ডিয়াল ইনফার্কশন
মায়োকার্ডিয়ামের রক্ত সরবরাহ বন্ধ হলে হার্ট অ্যাটাক হয়
এন্ডোকার্ডাইটিস
এন্ডোকার্ডিয়ামের প্রদাহ, সাধারণত ব্যাকটেরিয়া সংক্রমণে
c. Auriculo-ventricular Septum (অরিকুলো-ভেনট্রিকুলার সেপটাম)
🔍 গঠনগত বৈশিষ্ট্য
Fibrous Skeleton
- ডান ও বাম AV ভালভের মাঝে সংযোগ
- কার্ডিয়াক মাসল ফাইবারের জন্য attachment point
AV Node অবস্থান
- এই সেপটামের ডান পাশে অবস্থিত
- কার্ডিয়াক কন্ডাকশন সিস্টেমের অংশ
💡 এই সেপটামের অস্বাভাবিকতা Ebstein's anomaly এর কারণ হতে পারে
⚙️ কার্যকরী গুরুত্ব
💡 এই সেপটাম ছাড়া হৃদপিণ্ডের chambers গুলি আলাদা থাকতে পারত না
🔬 তুলনামূলক শারীরস্থান
| প্রাণী | AV Septum বৈশিষ্ট্য |
|---|---|
| মানুষ | সম্পূর্ণভাবে বিভক্ত, শক্তিশালী fibrous component |
| উভচর | অসম্পূর্ণ বিভাজন, কিছু mixing of blood |
| শিশু (ভ্রূণ) | Foramen ovale এর মাধ্যমে সংযোগ |
🫀 Fossa Ovalis (ফোসা ওভালিস)
ভ্রূণীয় সংবহনের গুরুত্বপূর্ণ অবশেষ
🔍 গঠনগত বৈশিষ্ট্য
- ইন্টারঅট্রিয়াল সেপটামের পোস্টেরিয়র অংশে অবস্থিত
- ডিম্বাকার গর্তের দাগ বা depression
- প্রায় 2-3 cm ব্যাস বিশিষ্ট
- Annulus ovalis দ্বারা বেষ্টিত
💡 Foramen ovale-এর অবশিষ্টাংশ, যা ভ্রূণীয় জীবনেই কাজ করত
🍼 ভ্রূণীয় অবস্থায় কাজ
ভ্রূণে রক্ত প্রবাহ
Right atrium → Foramen ovale → Left atrium
জন্মের পর
ফুসফুস সক্রিয় হলে foramen ovale বন্ধ হয়
👶 জন্মের পরের পরিবর্তন
💡 25% মানুষের ক্ষেত্রে foramen ovale সম্পূর্ণ বন্ধ হয় না (PFO)
🏥 ক্লিনিক্যাল তাৎপর্য
Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO)
- Foramen ovale সম্পূর্ণ বন্ধ না হওয়া
- 25% মানুষের মধ্যে দেখা যায়
- সাধারণত কোনো সমস্যা তৈরি করে না
প্যারাডক্সিক্যাল এম্বোলিজম
- PFO থাকলে রক্তের clot মস্তিষ্কে যেতে পারে
- Cryptogenic stroke এর কারণ হতে পারে
💡 PFO closure device দিয়ে বড় defects বন্ধ করা যায়
❤️ Chambers of the Mammalian Heart (স্তন্যপায়ী হৃদপিণ্ডের প্রকোষ্ঠসমূহ)
স্তন্যপায়ী প্রাণীদের হৃদপিণ্ডে ৪টি প্রকোষ্ঠ (4 Chambers) থাকে:
① Right Auricle / Right Atrium (ডান অলিন্দ)
🔹 Inlets (যেখানে রক্ত প্রবেশ করে):
১টি SVC (Superior Vena Cava) = pre-caval vein → শরীরের উপরের অংশ থেকে অপরিশোধিত (impure) রক্ত আনে
১টি IVC (Inferior Vena Cava) = post-caval vein → শরীরের নিচের অংশ থেকে অপরিশোধিত রক্ত আনে
১টি Coronary Sinus → হৃদপিণ্ডের নিজস্ব ভেন (coronary veins) থেকে রক্ত এনে ডান অলিন্দে ফেলে
🔹 Outlet (রক্ত বাহির হয়):
রক্ত ডান অলিন্দ থেকে right AV foramen (Auriculo-ventricular opening) দিয়ে Right Ventricle-এ প্রবেশ করে
② Right Ventricle (ডান নিলয়)
🔹 Inlet:
Right AV foramen দিয়ে ডান অলিন্দ থেকে রক্ত গ্রহণ করে
🔹 Outlet:
রক্ত Pulmonary Artery (ফুসফুস ধমনী) দিয়ে ফুসফুসে পাঠানো হয় অক্সিজেনেশনের জন্য
(❗ একমাত্র ধমনী যা অপরিশোধিত রক্ত বহন করে)
③ Left Auricle / Atrium (বাম অলিন্দ)
🔹 Inlet:
Pulmonary Veins (ফুসফুস শিরা) থেকে oxygenated (পরিশোধিত) রক্ত গ্রহণ করে
(❗ একমাত্র শিরা যা পরিশোধিত রক্ত বহন করে)
🔹 Outlet:
রক্ত Left AV foramen দিয়ে Left Ventricle-এ যায়
④ Left Ventricle (বাম নিলয়)
🔹 Inlet:
Left AV foramen দিয়ে বাম অলিন্দ থেকে রক্ত গ্রহণ করে
🔹 Outlet:
পরিশোধিত রক্ত Aorta (মহাধমনী) এর মাধ্যমে সারা শরীরের অঙ্গপ্রত্যঙ্গে পাঠানো হয় (Systemic Circulation)
🔶 Valves (ভালভ) – রক্তের সঠিক দিক নির্ধারণে বাধাহীন প্রবাহ রক্ষা করে
🔸 Right Atrium (ডান অলিন্দ):
🔹 এই কক্ষে রক্ত প্রবেশ করে তিনটি পথ দিয়ে:
- SVC (Superior Vena Cava)
- IVC (Inferior Vena Cava)
- Coronary Sinus
🔹 প্রতিটি openings-এর মুখে ভালভ থাকে, যাতে backflow (রক্ত ফিরে না যায়)।
| Opening | Valve Name | কাজ |
|---|---|---|
| SVC | Haversian Valve | উঁচু দেহাংশ থেকে রক্ত প্রবেশে পরে ফিরে যেতে বাধা দেয়। |
| IVC | Eustachian Valve | নিচু দেহাংশ থেকে আসা রক্তের জন্য গেট। |
| Coronary Sinus | Thebesian Valve | হৃদপিণ্ডের নিজস্ব ভেন থেকে রক্ত ঢোকার পথে থাকে। |
🧠 এই ভালভগুলো অনেক সময় অনুপস্থিত বা অকার্যকর হতে পারে কিন্তু ভ্রূণ অবস্থায় এদের বড় ভূমিকা থাকে।
🔸 Left Atrium (বাম অলিন্দ):
🔹 রক্ত এখানে আসে Pulmonary Veins (ফুসফুসের শিরা) দিয়ে।
🔹 মানুষের ক্ষেত্রে ৪টি pulmonary vein, খরগোশে (rabbit) ২টি vein।
🔸 এগুলোর কোনো ভালভ থাকে না, কারণ ফুসফুস থেকে রক্ত সহজেই প্রবাহিত হয় এবং ব্যাকফ্লো সাধারণত হয় না।
🧱 Walls (প্রাচীর বা দেয়াল): ভিতরের গঠন ও বৈশিষ্ট্য
🔸 Auricles (অলিন্দ বা Atria):
🔹 এখানে একধরনের transverse (আড়াআড়ি) পেশির রেখা থাকে – যাকে বলে Musculi Pectinati।
🔸 এগুলো combed muscle এর মতো দেখায় → দেখতে চিরুনির দাঁতের মতো।
🔸 Ventricles (নিলয়):
🔹 এর দেয়াল বেশ পুরু ও অসমান (rough)। কারণ নিচের গঠনগুলো থাকে:
🔹 1. Trabeculae Carneae / Columnae Carneae (ট্রাবেকুলি কারনেয়ি):
- এগুলো হল ভিতরের muscular ridges (মাংসপেশির রেখা)
- সংকোচনের সময় রক্তের প্রবাহে সহায়তা করে।
🔹 2. Papillary Muscles (প্যাপিলারি মাসল):
- এক প্রান্ত: ventricles-এর প্রাচীরে সংযুক্ত
- অন্য প্রান্ত: AV valve-এর ফ্ল্যাপের সঙ্গে সংযুক্ত থাকে Chordae Tendineae দ্বারা
🔹 3. Chordae Tendineae (কর্ডি টেন্ডিনি):
- তৈরি: Collagenous, inelastic (নমনীয় নয়) ফাইবার দিয়ে
- কাজ: AV Valve-এর ফ্ল্যাপকে atrium-এ ধাক্কা খেয়ে ওপরে উঠে যাওয়া থেকে রক্ষা করা
👉 অর্থাৎ, যখন ventricles সংকুচিত হয়, তখন এই স্ট্রিংগুলো ফ্ল্যাপকে ধরে রাখে যাতে রক্ত ওপরে না ফেরে।
🎯 মোট লাইনে মনে রাখার মতো ফর্মুলা:
| গঠন | অবস্থান | কাজ |
|---|---|---|
| Haversian Valve | SVC opening | Backflow রোধ |
| Eustachian Valve | IVC opening | Backflow রোধ |
| Thebesian Valve | Coronary Sinus opening | Backflow রোধ |
| Musculi Pectinati | Atria wall | Flow গাইড করে |
| Trabeculae Carneae | Ventricle wall | সংকোচনে সহায়তা |
| Papillary Muscle + Chordae Tendineae | AV Valve | Valve কে জায়গায় ধরে রাখে |
🌿 স্বয়ংক্রিয় স্নায়ুতন্ত্রের হৃদক্রিয়ার উপর প্রভাব
সিমপ্যাথেটিক বনাম প্যারাসিমপ্যাথেটিক নার্ভাস সিস্টেম
| 🔹 বিষয়বস্তু | ⚡ Sympathetic | 🧘♂️ Parasympathetic |
|---|---|---|
| মূল ভূমিকা | উত্তেজিত করে (Excites) | শান্ত করে (Calms) |
| কোন অংশে কাজ করে | SA Node, AV Node, Ventricular Muscles | SA Node, Atria (Ventricles-এ সামান্য) |
| Heart Rate (HR) | বাড়িয়ে দেয় (↑) | কমিয়ে দেয় (↓) |
| Force of Contraction | বাড়িয়ে দেয় (↑), বিশেষ করে ventricles-এ | উল্লেখযোগ্যভাবে পরিবর্তন করে না (≈) |
| Cardiac Output | বৃদ্ধি পায় (↑) | হ্রাস পায় (↓) |
| Baseline Role | হৃদপিণ্ডকে ৩০% বেশি সক্রিয় রাখে | বিশ্রামকালীন হার্ট অ্যাক্টিভিটি কমায় |
| Very Strong Stimulation | হৃদপিণ্ড খুব দ্রুত ও শক্তিশালীভাবে কাজ করে | কিছুক্ষণ হার্ট বন্ধ হয়ে যেতে পারে, তারপর ধীরে (20–40 bpm) কাজ শুরু করে |
| Clinical Impact | Exercise বা stress response-এ গুরুত্বপূর্ণ | বিশ্রাম ও ঘুমের সময় নিয়ন্ত্রণ করে |
⚡ সিমপ্যাথেটিক সিস্টেম
নিউরোট্রান্সমিটার:
নরএপিনেফ্রিন (Norepinephrine)
রিসেপ্টর:
β1-adrenergic receptors
(SA node, AV node, Ventricles)
🧘♂️ প্যারাসিমপ্যাথেটিক সিস্টেম
নিউরোট্রান্সমিটার:
অ্যাসিটাইলকোলিন (Acetylcholine)
রিসেপ্টর:
Muscarinic (M2) receptors
(প্রধানত SA node, কিছুটা AV node)
🏥 ক্লিনিক্যাল তাৎপর্য
β-ব্লকার ড্রাগস
(যেমন: Propranolol) - সিমপ্যাথেটিক ইফেক্ট ব্লক করে
ভেগাল ম্যানুভার
(যেমন: Valsalva) - প্যারাসিমপ্যাথেটিক অ্যাক্টিভিটি বাড়ায়
📌 স্বয়ংক্রিয় নিয়ন্ত্রণ সারাংশ
Fight or Flight
Rest & Digest
সামঞ্জস্য বজায় রাখে






.jpeg)
